프림 알고리즘과 크루스칼 알고리즘은 MST(Minimum Spanning Tree)를 구하는 알고리즘이다.
Spanning Tree 란 그래프 중 모든 정점이 간선으로 연결되어 있으면서 싸이클이 없는 그래프를 의미한다.
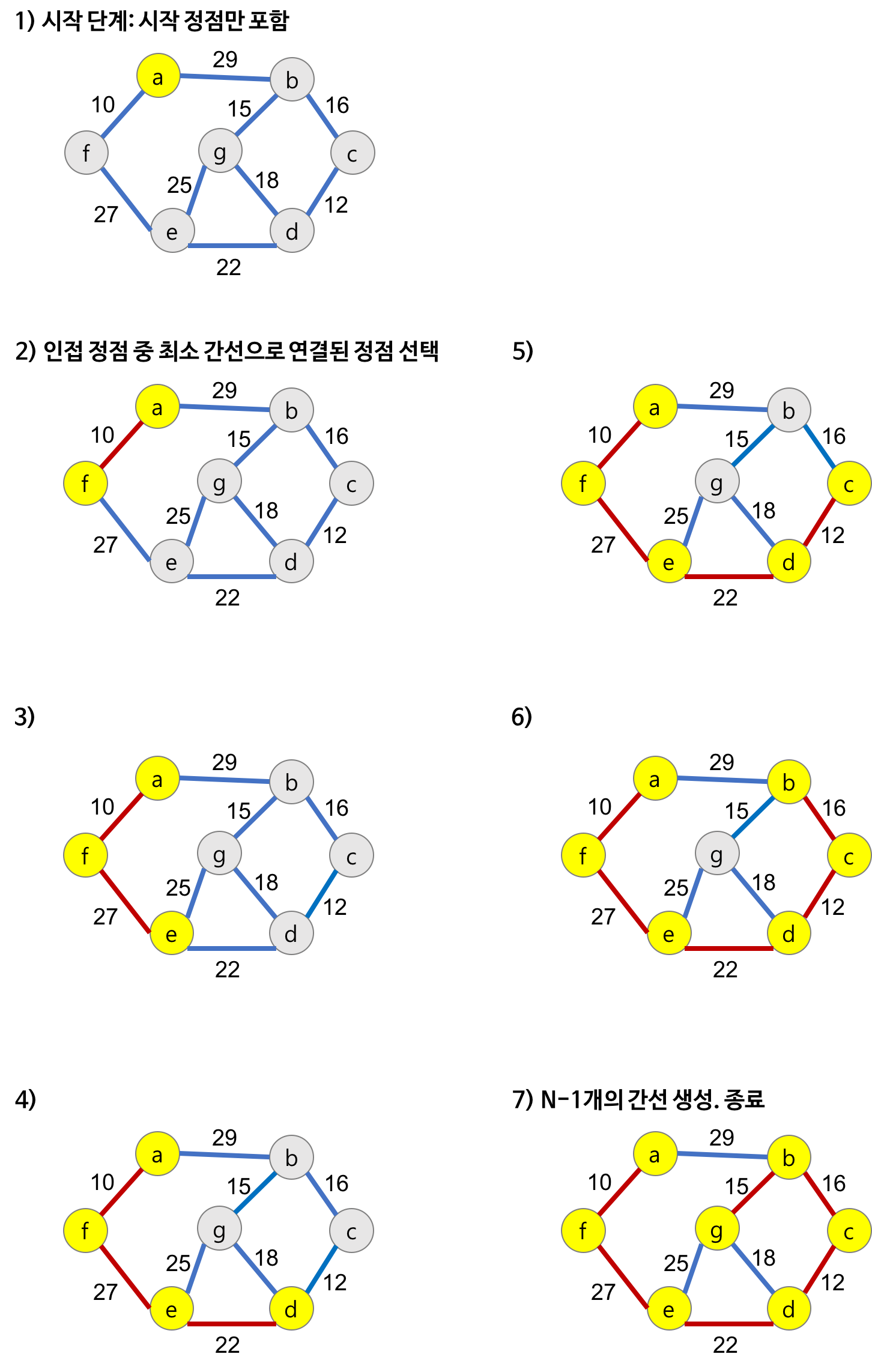
Prim 알고리즘은 시작 정점에서부터 출발해서 신장트리 집합을 단계적으로 확장해나가는 방법이다.
동작 순서
1. 시작 단계에서는 시작 정점만이 MST 집합에 포함된다.
2. 앞 단계에서 만들어진 MST 집합에 인접한 정점들 중에서 최소 간선으로 연결된 정점을 선택하여 트리를 확장한다.
3. n-1 개의 간선이 될 때까지 반복한다.
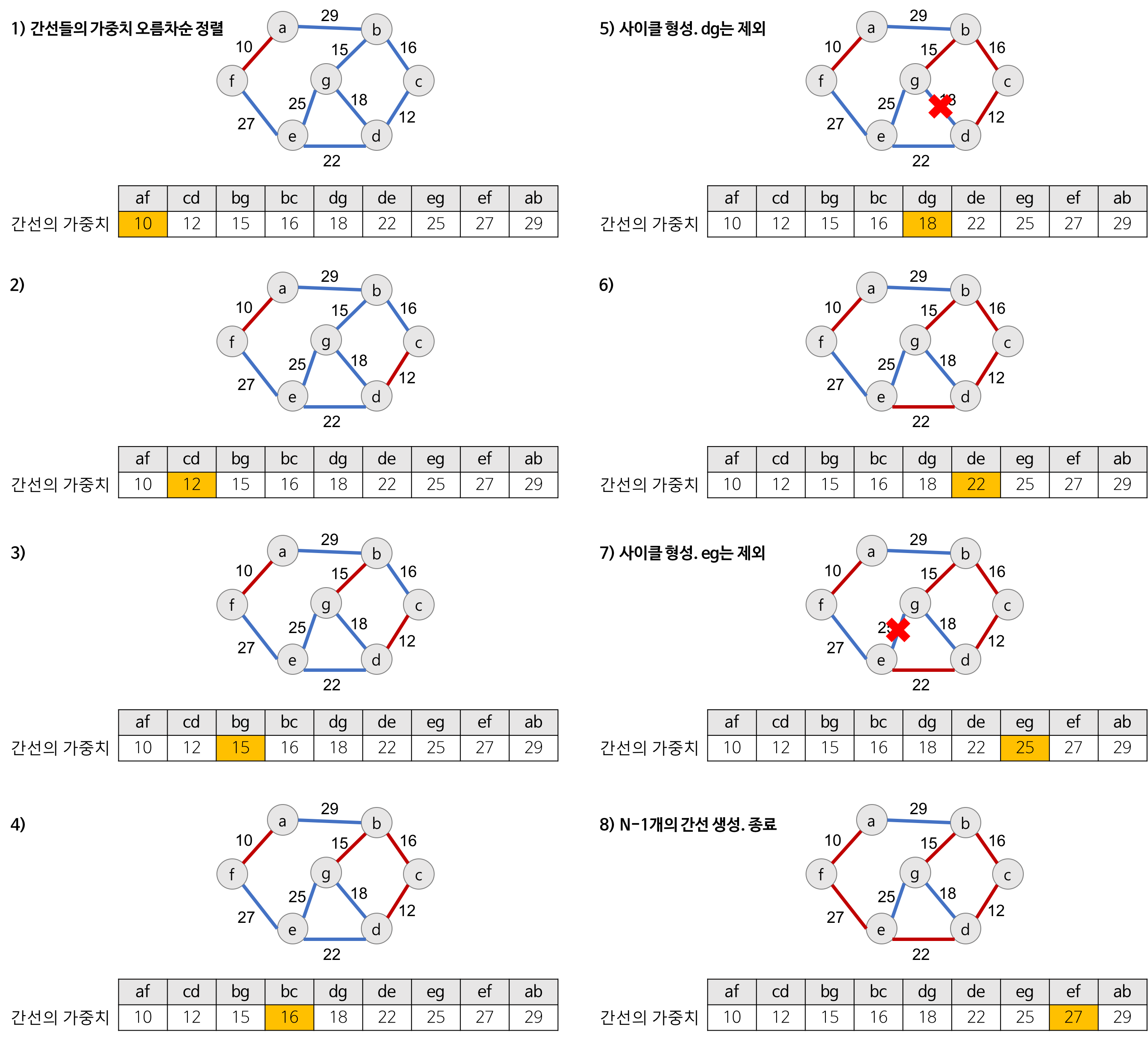
Kruskal 알고리즘은 간선 선택을 기반으로 하는 알고리즘이다.
동작 순서
1. 그래프의 간선들을 가중치의 오름차순으로 정렬한다.
2. 정렬된 간선 리스트에서 순서대로 사이클을 형성하지 않는 간선을 선택한다.
( 가장 낮은 가중치부터 선택하고 그 간선을 선택했을 때에 사이클을 형성하면 건너뛴다 )
3. 해당 간선을 현재의 MST의 집합에 추가한다.
여기서 싸이클 형성 여부는 유니온 파인드 알고리즘을 사용한다.
Prim은 O(n^2)
Kruskal은 O(elog2e) 이므로
적은 숫자의 간선만을 가지는 희소 그래프의 경우 Kruskal,
그래프에 간선이 많이 존재하는 밀집 그래프의 경우는 Prim 이 적합하다.
크루스칼 알고리즘은 탐욕적인 방법을 이용해서 그래프의 모든 정점을 최소 비용으로 연결하는 답을 구하는 것이다.
탐욕적 방법은 그 순간에는 최적이지만, 전체적인 관점에서 최적이라는 보장이 없어서 검증을 해야하지만, 크루스칼 알고리즘은 최적의 해답을 주는 것으로 증명되어있다고 한다.
유니온 파인드에 대해서는
[Algorithm] 유니온 파인드(Union - Find)
유니온 파인드 알고리즘이란? 그래프 알고리즘의 일종으로서 상호 배타적 집합, Disjoint-set 이라고도 합니다. 여러 노드가 존재할 때 어떤 두 개의 노드를 같은 집합으로 묶어주고, 다시 어떤 두 �
ssungkang.tistory.com
설명을 너무 잘해놓은 티스토리가 있어 링크를 남긴다.
유니온 파인드 구현
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
|
public class test{
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
int[] parent=new int[9];
Arrays.fill(parent, -1);
union(parent, 1, 2);
union(parent, 2, 3);
union(parent, 3, 4);
union(parent, 4, 5);
union(parent, 6, 6);
union(parent, 7, 8);
System.out.println(isCycle(parent, 1, 4));
}
public static int find(int[] parent, int a) {
if (parent[a] < 0) {
return a;
} else {
return parent[a] = find(parent, parent[a]);
}
}
public static void union(int[] parent, int x, int y) {
x = find(parent, x);
y = find(parent, y);
if(x==y) return;
if (parent[x] < parent[y]) {
parent[x] += parent[y];
parent[y] = x;
} else {
parent[y] += parent[x];
parent[x] = y;
}
}
public static boolean isParent(int[] parent, int x, int y) {
int a = find(parent, x);
int b = find(parent, y);
return a==b;
}
}
|
cs |
프림 알고리즘 구현 (프로그래머스 섬연결하기 문제를 프림 알고리즘으로 풀어봄)
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
|
public static class Edge implements Comparable<Edge> {
public int to; public int weight; public Edge(int to, int weight) { this.to = to; this.weight = weight; } @Override public int compareTo(Edge o) { return this.weight - o.weight; } } public static int solution(int n, int[][] costs) { int[][] adj = new int[n][n]; //인접행렬 for (int[] cost : costs) { adj[cost[0]][cost[1]] = cost[2]; adj[cost[1]][cost[0]] = cost[2]; } return prim(n, adj); } private static int prim(int n, int[][] adj) { PriorityQueue<Edge> pq = new PriorityQueue<>(); boolean[] visit = new boolean[n]; int currentEdge = 0; int totalWeight = 0; while (true) { visit[currentEdge] = true; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { if (adj[currentEdge][i] != 0 && !visit[i]) { pq.add(new Edge(i, adj[currentEdge][i])); } } currentEdge = -1; while (!pq.isEmpty()) { Edge edge = pq.poll(); if (!visit[edge.to]) { totalWeight += edge.weight; currentEdge = edge.to; break; } } if (currentEdge == -1) { break; } } return totalWeight; } //int currentEdge가 아니라 Queue를 이용해도 됨 private static int prim(int n, int[][] adj) { Queue<Integer> edgeQue = new LinkedList<>(); PriorityQueue<Edge> pq = new PriorityQueue<>(); boolean[] visit = new boolean[n]; edgeQue.add(0); int totalWeight = 0; while (!edgeQue.isEmpty()) { Integer currentEdge = edgeQue.poll(); visit[currentEdge] = true; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { if (adj[currentEdge][i] != 0 && !visit[i]) { pq.add(new Edge(i, adj[currentEdge][i])); } } while (!pq.isEmpty()) { Edge edge = pq.poll(); if (!visit[edge.to]) { edgeQue.add(edge.to); totalWeight += edge.weight; break; } } } return totalWeight; } |
cs |
|
|
|
크루스칼 알고리즘 구현 (프로그래머스 섬 연결하기 문제를 크루스칼 알고리즘으로 풀어봄)
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
|
public static class Edge implements Comparable<Edge> {
public int from; public int to; public int weight; public Edge(int from, int to, int weight) { this.from = from; this.to = to; this.weight = weight; } @Override public int compareTo(Edge o) { return this.weight - o.weight; } } public static int solution(int n, int[][] costs) { int totalWeight = 0; int[] parent = new int[n]; List<Edge> edges = new ArrayList<>(); Arrays.fill(parent, -1); for (int[] cost : costs) { edges.add(new Edge(cost[0], cost[1], cost[2])); } Collections.sort(edges); for (Edge edge : edges) { if (isCycle(edge.to, edge.from, parent)) { continue; } totalWeight += edge.weight; union(edge.to, edge.from, parent); } return totalWeight; } private static void union(int a, int b, int[] parent) { int aRoot = find(a, parent); int bRoot = find(b, parent); if (aRoot == bRoot) { return; } if (aRoot < bRoot) { parent[bRoot] += parent[aRoot]; parent[aRoot] = bRoot; return; } parent[aRoot] += parent[bRoot]; parent[bRoot] = aRoot; } private static boolean isCycle(int to, int from, int[] parent) { return find(to, parent) == find(from, parent); } private static int find(int node, int[] parent) { if (parent[node] < 0) { return node; } return parent[node] = find(parent[node], parent); } |
cs |
유니온 파인드에서 조금만 변형을 해주면 된다.
ArrayList 대신 PriorityQueue를 이용해도 된다.
'Java' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Java System.arraycopy() 에 대해 (0) | 2020.09.11 |
|---|---|
| Java 다익스트라 알고리즘(Dijkstra Algorithm)에 대해 (0) | 2020.09.08 |
| 자바에서 volatile 이란? (0) | 2020.09.04 |
| 위상정렬 자바로 구현하기, 백준2252_줄 세우기 (0) | 2020.08.31 |
| Java Trie(트라이)란 (0) | 2020.08.27 |
